According to the 1986 Environmental Protection Act and the newly revised Solid Waste Management Rules in 2026 (which officially came into effect on April 1), India has coordinated the management of household waste through the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), and implemented mandatory "four category source sorting" (wet waste, dry waste, sanitary waste, and special care waste). It is explicitly required to achieve zero landfill of urban household waste by 2030, and environmental compensation fees will be levied based on the "polluter pays" principle for illegal disposal. The current dilemma of garbage disposal in India is prominent, with giant garbage mountains scattered throughout core cities such as New Delhi and Mumbai. Among them, the Ghazipur garbage mountain in New Delhi is as high as 60 meters and frequently experiences fires and landslides. The Dionne garbage mountain in Mumbai has a history of nearly a century of accumulation. The daily production of household waste in the country is about 158000 tons, with an average of 500 grams per person per day in New Delhi. Wet waste (organic waste) accounts for 58% of the waste, containing a large amount of food residues and by-products from rice processing. The entire region has a tropical monsoon climate, with high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and high humidity. Garbage is prone to spoilage and decay, producing foul odors and leachate, polluting the soil and water systems such as the Ganges and Yamuna rivers. At the same time, India's waste management infrastructure is weak, with a severe shortage of specialized landfills. Many existing incineration plants are not suitable for the environment, and the high proportion of wet waste leads to insufficient calorific value and difficulty in incineration. There is an urgent need for efficient, low-cost, easy to operate, and energy-efficient treatment equipment that adapts to the characteristics of local waste.
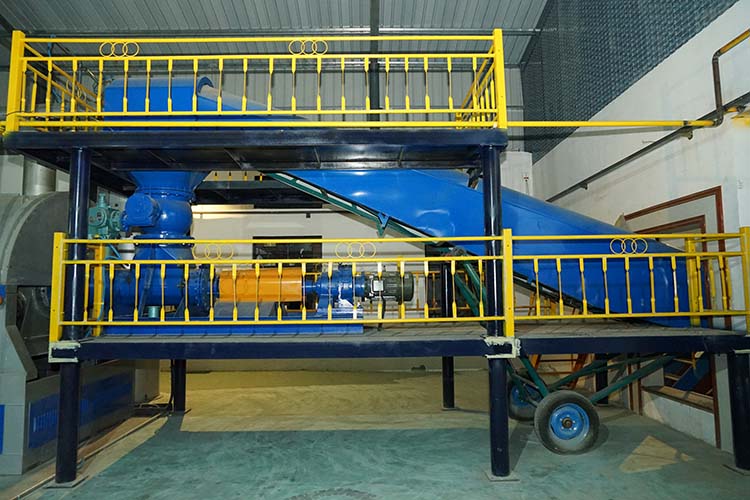

China Yongle Environmental Protection Engineering has developed a targeted "printed label high-efficiency sorting energy" household waste treatment equipment: using anti-corrosion and wear-resistant cabin body+anti leakage structure, it can withstand high temperature and high humidity environment, equipped with high-efficiency dust removal and desulfurization module, and emission indicators fully comply with CPCB national environmental standards. It has been registered with the municipal departments of New Delhi and Mumbai, and is suitable for dual scenarios of garbage mountain management and decentralized treatment. Equipped with a "grid diesel dual drive+intelligent sorting system", it intelligently identifies wet, dry, sanitary, and special waste, automatically completes sorting without a large amount of manual intervention, and is equipped with a bilingual operation interface in Hindi and English. Real time data is uploaded and processed to the CPCB supervision platform, meeting compliance traceability requirements. The core adopts a dual process of "high-temperature anaerobic fermentation+garbage incineration power generation". Wet garbage fermentation can produce biogas (methane content ≥ 65%) after 10 days, which can be directly connected to local small-scale power plants; After sorting, the combustible part of the dry garbage is used for incineration power generation, while the non combustible part is recycled and reused. The incineration ash is solidified and used as infrastructure filling material, with an overall resource utilization rate of 86%. This effectively solves the pain points of high proportion of wet garbage and difficult incineration in the local area, avoiding garbage mountain accumulation and leachate pollution.
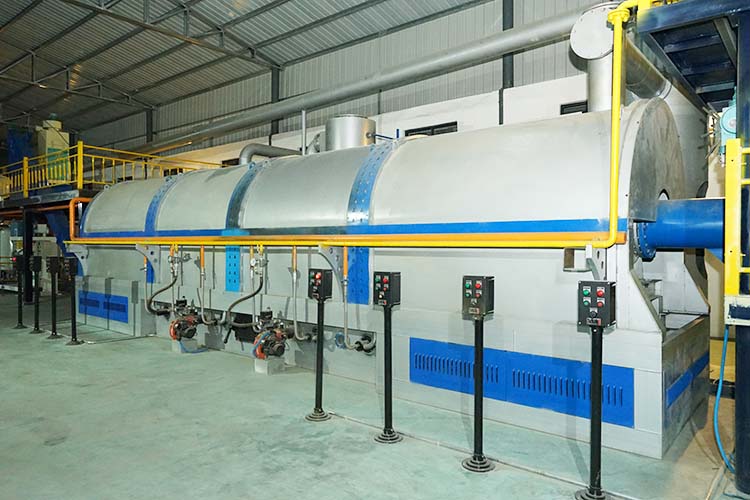

Adapting to the needs of India: At the Okhla waste incineration plant in New Delhi, the cluster equipment optimizes the incineration process, adds auxiliary combustion agents to increase the calorific value, and has a daily processing capacity of 180 tons, significantly reducing harmful gas emissions such as dioxins and helping to reduce the amount of waste in Ghazipur; At the Mumbai urban garbage transfer station, the large equipment has a daily processing capacity of 220 tons and is accurately connected to the four classification sorting system to quickly process accumulated garbage and reduce the spread of odors; In cities such as Bangalore and Gurgaon, modular equipment is integrated into local waste recycling networks, producing electricity that is directly supplied to surrounding communities, reducing the pressure on the power grid; In rural and remote areas, small mobile devices have a daily processing capacity of 15 tons. Diesel powered devices do not require a stable power grid, and the organic fertilizer produced by wet garbage fermentation is directly supplied to surrounding farmland, suitable for grassroots scenarios dominated by agriculture; In religious holy sites such as Rishigesh, equipment is equipped with silent and deodorizing modules to avoid polluting tourism resources and religious sites.

Local compliance and service guarantee: The equipment strictly complies with the new solid waste management rules of 2026, adapts to the requirements of four classification sorting and energy transformation, and can help enterprises fulfill extended producer responsibility (EPR) and enjoy relevant tax exemptions. Set up large service bases in New Delhi and Mumbai, reserve wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant core spare parts, achieve a 3-hour maintenance response in core cities, and provide on-site maintenance services in remote areas. We provide bilingual training in Hindi and English, as well as interpretation of CPCB regulations, to assist clients in completing compliance filing. The energy consumption of equipment operation is 45% lower than traditional equipment, and it can participate in carbon credit trading. At the same time, we optimize the operation and maintenance process, adapt to the shortage of technical talents in India, significantly reduce operation and maintenance costs, help India solve the garbage mountain dilemma, and promote the implementation of the "Clean India 2.0" plan.
Yongle Environmental Protection is mainly engaged in the research and development, production and sales of complete sets of technical equipment for organic solid waste disposal and comprehensive utilization. Production and manufacturing, domestic waste treatment equipment, tire pyrolysis equipment, medical waste disposal equipment, hazardous waste disposal equipment, and achieve efficient and comprehensive utilization of resources through independently developed low-temperature anaerobic pyrolysis equipment technology solutions.
Tags:Efficient sorting of printed waste equipment helps with energy utilization,household waste treatment equipment,YONGLE GROUP
 Latest news
Latest news